RFID tags with frequency conversion and electromagnetic energy harvesting Acronym: TagME |
|
| ❚ Ro ❚ Eng | |
Project title: RFID tags with frequency conversion and electromagnetic energy harvesting
Acronym: TagME
PN IV Program: Program 5.2 – Human Resources; Subprogram 5.2.1 – Start in Research
Project Type: Research Projects for Young Independent Teams - 2023 Call
Contract nr. 27TE/2025/08.01.2025 (code: PN-IV-P2-2.1-TE-2023-1239)
Project Duration: 08.01.2025-31.12.2026
Project Budget: 499.996,00 RON
Contractor: National Institute of Research and Development in Microtechnologies – IMT Bucharest (www.imt.ro)
Contracting Authority: Executive Agency for Higher Education, Research, Development and Innovation Funding – UEFISCDI (www.uefiscdi.gov.ro)
Project director: Dr. Alina-Cristina BUNEA (alina.bunea@imt.ro)
Project summary:
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is among the key enabling technologies of the Internet of Things (IoT) concept. RFID technology has been extensively implemented for tagging, locating, sensing, and tracking objects across a wide range of fields, including retail, logistics, healthcare, automotive and agriculture.
The main goal of the project is the development and implementation of a new family of harmonic RFID tags with frequency conversion and electromagnetic energy harvesting capabilities and compact metasurface enhanced antennas. The targeted frequency range will be 2-12 GHz.
The main objectives are related to the design, fabrication, and experimental characterization of metasurface enhanced microwave antennas (O1); frequency conversion circuits with amplification of the output signal using energy harvesting (O2); demonstrator integrating the microwave antennas with the frequency conversion circuits (O3).
The project aims to advance the knowledge of the fields of IoT and RFID by developing new concepts and approaches for the harmonic transponder with energy harvesting/wireless power transfer for output signal amplification and compact metasurface enhanced antennas. The demonstration of the new family of circuits with battery-free operation, increased readout range, reduced size and relatively low cost is expected to have significant impact for the next generations of sustainable eco-friendly, wireless interconnected IoT devices.
Team:
Project leader:
Dr. Alina-Cristina Bunea received the B.Sc. (2009), M.Sc. (2011) and Ph.D. (2016) degrees from the “Politehnica” University of Bucharest, Romania. She is currently working as a senior research scientist (CS1) at IMT Bucharest, where she is involved in the design, 3D electromagnetic modeling and characterization of passive and active microwave circuits. She was a key team member in 13 research projects, led 3 national projects and is currently leading an international project and two national projects and is involved in the National Platform for Semiconductor Technologies (PNTS, www.imt.ro/pnts). She has authored over 60 peer reviewed papers in the research field of the project and has an h-index of 10 (Google scholar, over 430 citations). Her main expertise lies in the design, modeling and characterization of microwave devices.
Team members:
Dr. Martino Aldrigo received the Ph.D. degree in electronic engineering, telecommunications, and information technology from the Faculty of Engineering, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy, in 2014. Since 2022, he has been a Principal Researcher II with IMT-Bucharest, Voluntari, Romania. He has co-authored more than 70 articles in ISI ranked journals and conferences with over 1000 citations and a h-index of 20. His main expertise comprises the electromagnetic simulation and experimental characterization of RF/microwave/millimeter-wave/terahertz systems for wireless/energy-harvesting applications embedding carbon-based, 2-D, and nanoscale ferroelectric materials.
Dr. Damir Mladenovic received his PhD degree in March 2023 in physics from the University of Bucharest. Faculty of Physics. Since 2016 he has been working in the Laboratory for Carbon Based Nanotechnologies and Nanostructures at IMT Bucharest. He has extensive expertise in mask design for direct laser writing as well as technological processing of chromium-on-glass-substrate based masks.
Prof. Dr. Dan Neculoiu graduated in 1985 and received his PhD degree in 1997, both from the “Politehnica” University of Bucharest (PUB), Romania. He is currently working as a senior research scientist at IMT-Bucharest and a full professor at the National University of Science and Technology POLITEHNICA Bucharest, Faculty of Electronics, Telecommunications and Information Technology. His main research areas are the design, modeling and measurements of microwave circuits, membrane supported millimeter wave filters, antennas and receiver modules, piezoelectric FBAR and SAW structures, and graphene-based microwave circuits. He participated in more than 25 national and international (FP4, FP6, FP7) research projects. He is the author of more than 150 papers published in journals and Conference Proceedings, with over 1880 citations, and a h-index of 22 (Google scholar). He will assist the young research team as a senior expert in the field of the project.
Objectives:
The main goal of the project is the development and implementation of a new family of harmonic RFID tags with frequency conversion and electromagnetic energy harvesting capabilities and compact metasurface enhanced antennas. The targeted frequency range will be 2-12 GHz.
The main objectives:
O1. The design, fabrication, and experimental characterization of metasurface enhanced microwave antennas;
O2. Development of frequency conversion circuits with amplification of the output signal using energy harvesting;
O3. Development of a demonstrator integrating the microwave antennas with the frequency conversion circuits.
Results:
Stage 1/2025:
During the reporting period, slot antennas operating at 2.5 GHz and in a dual-band regime (around 2.5 GHz and 5 GHz), along with slot-type and strip-type ELC metasurfaces were designed, modeled 3D and electromagnetically simulated. Test structures were fabricated on FR-4 substrates, 1.55 mm thick, copper-clad. The antennas were characterized in the microwave domain using a vector network analyzer, and their matching bandwidths were extracted. For the 2.5 GHz slot antenna, the fractional matching bandwidth is approximately 20%. For the dual-band antenna, the matching bandwidths are 45% at 2.5 GHz and 6.4% at 5 GHz.
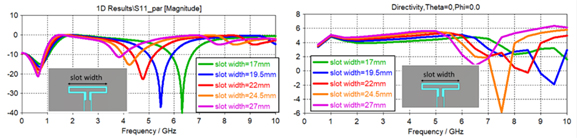
Parametric simulations for the 5 GHz slot-antenna model: effect of the slot width (parameter slot_width) on the S11 parameter (left) and on the directivity in the direction normal to the antenna plane, as a function of frequency (right).
Using the two-antenna method, the frequency-dependent gain was estimated for both antenna types. By combining transmission measurements with an experimental setup incorporating a goniometric system, 2D radiation characteristics corresponding to the magnetic (H-plane) and electric (E-plane) were obtained. Antennas placed above ELC slot-type and strip-type metasurfaces were characterized, and the effects associated with different configurations were documented.

Measurement setup with monopole antenna (left) and the test slot antenna (right) mounted on the goniometric holder
A frequency-doubling circuit with a 2.5 GHz input frequency and RF-to-DC conversion was designed using nonlinear simulations. The circuit is microstrip-based and was designed for PCB substrate fabrication. Test circuits were manufactured on Rogers 4003C substrate, 1.5 mm thick, double-clad with 35 µm copper. These circuits were assembled with SMD components (inductors, capacitors, resistors) and a Schottky diode (Skyworks SMS7630), and equipped with SMD connectors. The circuit was subsequently characterized in both DC and RF, yielding experimental results in good agreement with simulations.

Experimental setup for the characterization of the frequency-conversion and energy-harvesting circuit
Two deliverables were completed (Deliverable D1 – Scientific Report for Stage 1/2025 and Deliverable D2 – Measured Performance of the Test Antennas), an IEEE conference paper acknowledging project support was published, and a journal paper is currently in preparation.
Dissemination:
- Mirela Şorecău; Emil Şorecău; Alina-Cristina Bunea; Dan Neculoiu; et al., „Software-Defined Radio System for Drone Detection: Preliminary Testing”, 2025 International Semiconductor Conference (CAS), Sinaia, Romania, 2025, pp. 87-90, doi: 10.1109/CAS66707.2025.11222205 – underlined the authors involved in the TagME project