Results:
List of synthetic indicators
26 indicators were obtained within the project duration, as follows:
A. Articles (ISI) – 2 articles
1) Gabriel MOAGǍR-POLADIAN, Victor MOAGǍR-POLADIAN, Raluca GAVRILǍ – “Field Effect Transistor-based Pressure Sensors with Highly Deformable Gate Dielectric Enabled by Additive Manufacturing”, sent to Flexible and Printed Electronics, IOP Publishing
2) Gabriel MOAGǍR-POLADIAN, Kalyan Yoti MITRA, Dana MITRA, Robert THALHEIM, Ralf ZICHNER, Victor MOAGǍR-POLADIAN, Cristina PACHIU, Niculae DUMBRǍVESCU, Dan VASILACHE – “Apparent semiconductor-to-metal-like transition of inkjet printed PEDOT:PSS track embedded in polymer under temperature variation”, sent to Flexible and Printed Electronics, IOP Publishing
Patent applications:
1. G. Moagăr-Poladian, V. Moagăr-Poladian – “Pressure sensor using field effect transistor with elastomeric dielectric”, OSIM A00342 / 16.06.2022
The invention refers to a pressure sensor that uses field effect transistor (either MOS version or TFT version) that can use up to three different sensing mechanisms for enhancing the sensitivity. The sensor can be made either in traditional CMOS / MEMS technology or by using inkjet techniques.
2) G. Moagăr-Poladian – “Electromagnetic radiation sensor using the control of losses in electrical transformer”, OSIM A00343/16.06.2022
The invention considers an electromagnetic radiation sensor that uses as a sensing mechanism the control of losses in a planar electric transformer.
3) G. Moagǎr-Poladian – “Bolometer-type infrared sensor using organic materials and procedure for its fabrication using additive manufacturing”, OSIM A00791 / 05.12.2022
The invention refers to a bolometric type infrared sensor that uses organic materials as sensing element and to a procedure of its fabrication by using additive manufacturing.
C. Conference presentations (with ISI Proceedings) – 1 conference
1) G. Moagǎr-Poladian, V. Moagǎr-Poladian – “Field effect transistor-based pressure sensor with dielectric elastomer, for robotic hand”, Proceedings of the International Semiconductor Conference 2022, p. 273-276, (2022)
Abstract: We present a pressure sensor based on a field effect transistor having improved performance compared to its fully inorganic counterparts. Key to it is the use of elastomers (in particular, PDMS) as the gate dielectric.
D. Demonstrators – 6 demonstrators
1) Sensor of electromagnetic radiation
A sensor of electromagnetic radiation was realized and tested. The sensor can work both in photonic and in photothermal regime. It is based on a semiconductor particle – insulating polymer composite.
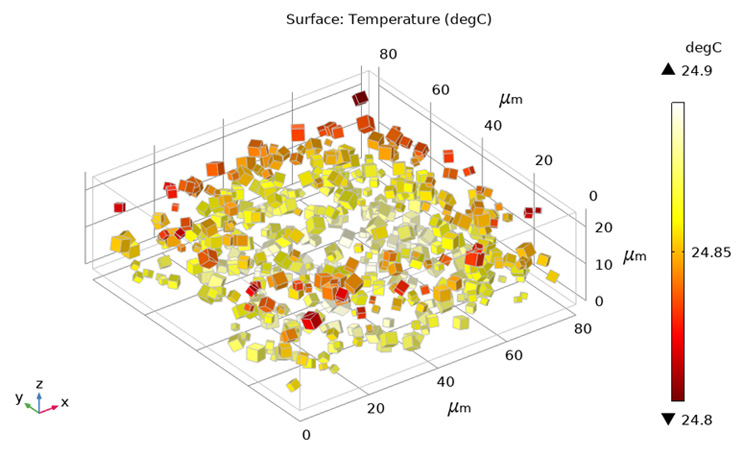
Temprature distribution on the surface of the semiconductor particles embedded in a polymer matrix; regime of thermal sensor
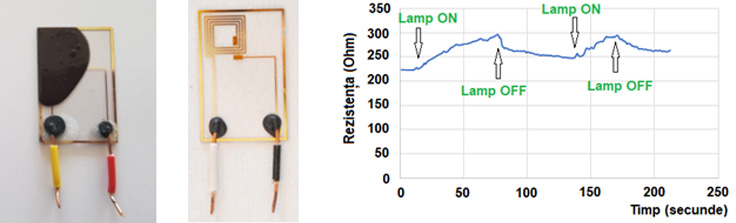
Photo image of the sensor (left and center) and of its response curve (right) under infrared lamp illumination.
2) Pressure sensor
A semiconducting particle-polymer composite based pressure sensor was made and tested.
3) Infrared sensor
It is a low cost infrared sensor made by using three additive manufacturing techniques. It is a bolometer type sensor.
4) UV sensor
A UV sensor using a composite of ZnO nanoparticles in a polymer.
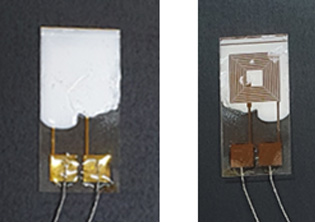
Photo image of the UV sensor based on ZnO-polymer composite. Left: image from above; Right: image from back of the sensor
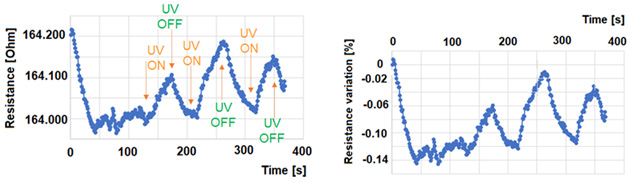
Graphs showing the resistance variation of the ZnO-polymer UV sensor under illumination with radiation at 295 nm. Left: absolute resistance values; Right: relative variation of resistance. The resistance increases at illumination, as expected from sensors using the devised sensing principle. The sensor has a responsivity of 2 Ohm/W or, equivalently, 0,5 S/W.
5) Optimized, bolometer type infrared sensor
It is a low cost infrared sensor, an optimized version of a previous one.
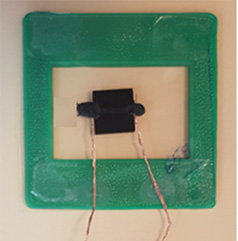
Photo image of the optimized , “toy”-like infrared detector (bolometer). It has a 0.1 % resistance variation when looking at a 5 cm diameter blackbody at 100 oC from a distance of 50 cm.
6) Thermopile type infrared sensor
It is a low cost infrared sensor that produces 1 mV voltage at a current of 1 µA when illuminated with an infrared lamp.
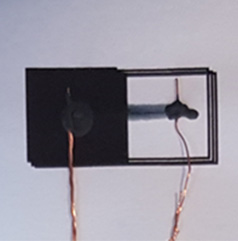
Photoimage of the „toy”-like thermopile (the whole device is 2 cm x 1 cm, on paper)
E. Technologies devised and developed – 3 technologies
1) Technology for fabrication of inductive effect based pressure sensors
The technology was devised and tested for the fabrication of a pressure sensor that uses the inductive effect of eddy currents in a semiconductor particle – polymer composite.
2) Technology for the fabrication of electromagnetic radiation sensors that use eddy current, two versions
The technology was devised and tested for the two versions of the inductor, one using a simple planar inductor and the other one using the modulation of losses in an electrical transformer.
3) Technology for fabrication of infrared sensor
It is a technology that uses three low cost additive fabrication technologies for the fabrication of thermal type infrared sensors.
F. Studies performed within the project – 9 studies
1. Development of an original concept of infrared sensor based on semiconductor particles composites
2. Experimental model of a humidity sensor
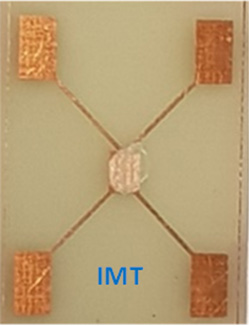
Photo image of the humidity sensor.
3. Experimental study regarding the production of Silicon with enhanced piezoresistive effect
4. Study regarding the main block components of the sensor printing robot
5. Study regarding the realistic CAD modelling of a photopolymer-semiconductor particle composite
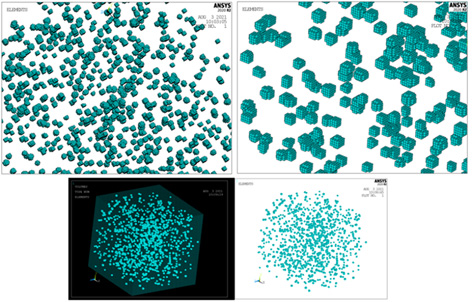
CAD model of the particles used for the composite simulation. Top left: the shape and space distribution of the particles inside the composite; Top right: detail showing the shape of the particles; Bottom left: the spatial distribution of the particles in the cube of composite; Bottom right: the same image, but without the representation of the cube.
6. Study of all-Silicon composites
7. Study regarding the apparent semiconductor-metal transition in insulator/organic semiconductor/insulator structures when temperature varies; deciphering of its mechanism
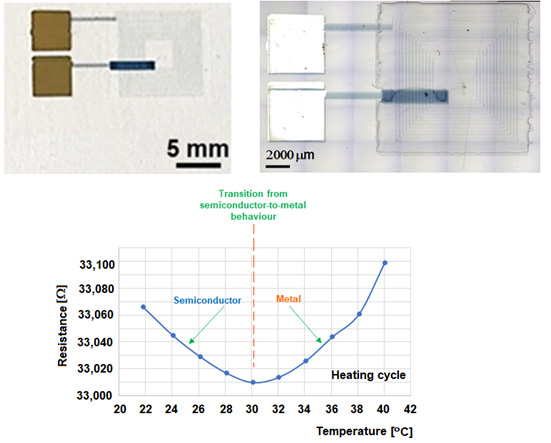
Image of the planar inductor made by inkjet printing using PEDOT:PSS as conductive track (top).
The resistance-vs.-temperature variation of the PEDOT:PSS planar inductor embedded in epoxy (bottom).
Table 5 – Comparison between measured and computed resistance values
Temperature ( oC) |
Calculated (Ohm) |
Measured (Ohm) |
Relative error (%) |
24 |
33077.34079 |
33045 |
0.097 |
26 |
33073.56121 |
33029 |
0.134 |
28 |
33069.77958 |
33017 |
0.159 |
30 |
33066 |
33010 |
0.169 |
32 |
33062.21837 |
33014 |
0.146 |
34 |
33058.43675 |
33026 |
0.098 |
36 |
33054.65716 |
33044 |
0.032 |
38 |
33050.87554 |
33061 |
- 0.030 |
40 |
33031.97354 |
33099 |
- 0.202 |
8. Detailed study of pressure sensors based on field effect transistors using deformable materials/structures as gate dielectric and of their characteristics, benefits, limitations and fabrication possibilities
9. Development of the algorithm for real-time, in-situ determination of the wear degree of the sensors printed on the robotic arm; development of the in-situ calibration procedure for the freshly deposited sensors
G. Other indicators (supplementary indicators) – 2 indicators
1. Mini-system for the characterization of sensors with respect to temperature
Designed, made, tested and used for the characterization of the sensors made within the project.
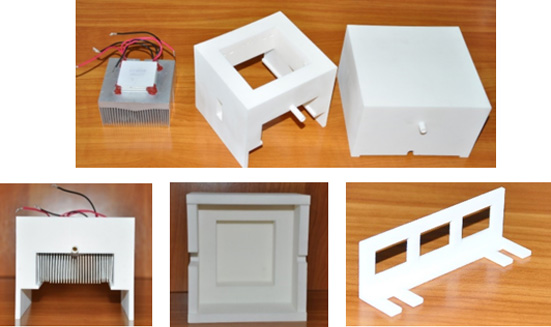
Photo image of the modules of the mini-system characterization of sensors with respect to temperature
2. System for the characterization of pressure / force sensors
It is based on a commercial bio-plotter. The adaptation for measuring pressure / force sensors was designed and made
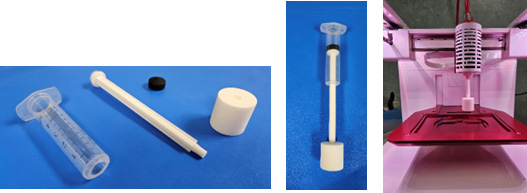
Photo image of the system for characterization of pressure / force sensors. Left: force / pressure application unit disassembled; Center: assembly for applying force / pressure; Right: the system assembled.
